Carboxylic Acid Derivatives Reactivity Order
11.4: The Relative Reactivity of Carboxylic Acrid Derivatives
- Folio ID
- 106360
In carboxylic acid derivatives, the fractional positive charge on the carbonyl carbon is stabilized past electron donation from nonbonding electrons on the adjacent heteroatom, which has the event of decreasing electrophilicity.

Amidst the carboxylic acrid derivatives, carboxylate groups are the least reactive towards nucleophilic acyl substitution, followed by amides, so carboxylic esters and carboxylic acids, thioesters, and finally acyl phosphates, which are the most reactive amidst the biologically relevant acyl groups. Acid anhydrides and acrid chlorides are laboratory reagents that are analogous to thioesters and acyl phosphates, in the sense that they likewise are highly reactive carboxylic acid derivatives. Section 11.viii most the end of this chapters includes information about the chemistry of these 2 reagents.
Relative reactivity of carboxylic acid derivatives:
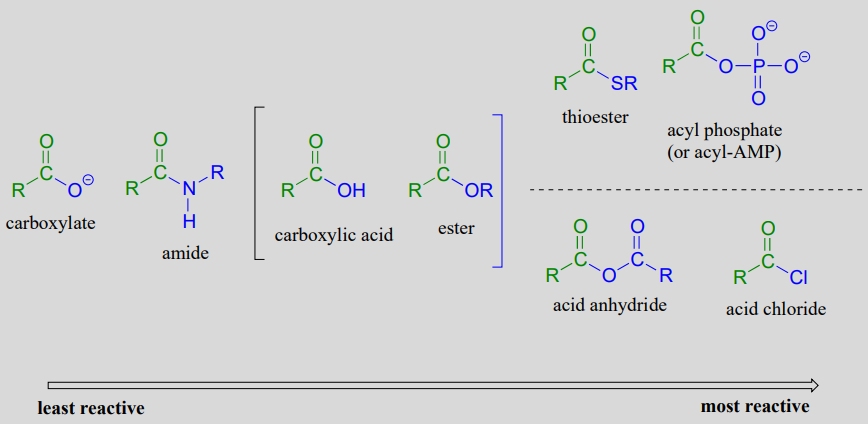
The reactivity trend of the carboxylic acid derivatives tin be understood by evaluating the basicity of the leaving grouping (acyl X group) - remember from section eight.4 that weaker bases are ameliorate leaving groups. A thioester is more reactive than an ester, for example, because a thiolate (RS-) is a weaker base and better leaving group than an alcoxide (\(RO\)-). Recall from affiliate seven that the \(pK_a\) of a thiol is well-nigh 10, while the \(pK_a\) of an alcohol is xv or higher: a stronger conjugate acrid means a weaker conjugate base.
In general, if the incoming nucleophile is a weaker base of operations than the 'acyl X' grouping that is already there, information technology volition likewise exist the better leaving group, and thus the kickoff nucleophilic pace volition simply opposite itself and we'll get the starting materials dorsum:
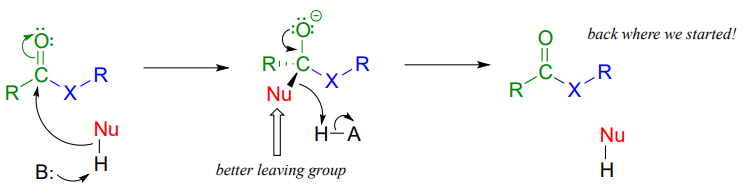
In full general, acyl substitution reactions convert college energy carboxylic acid derivatives into derivatives of lower energy. Thioesters, for example, are oft converted directly into carboxylic esters in biochemical reactions, only not the other way around. To go 'uphill' - from a carboxylate to a thioester, for example, requires the 'coupling' of the uphill reaction to an energetically favorable reaction. We will encounter how this works in the next section.
Carboxylic Acid Derivatives Reactivity Order,
Source: https://chem.libretexts.org/Bookshelves/Organic_Chemistry/Book%3A_Organic_Chemistry_with_a_Biological_Emphasis_v2.0_(Soderberg)/11%3A_Nucleophilic_Acyl_Substitution_Reactions/11.04%3A_The_Relative_Reactivity_of_Carboxylic_Acid_Derivatives#:~:text=Among%20the%20carboxylic%20acid%20derivatives,the%20biologically%20relevant%20acyl%20groups.
Posted by: avilatheed1963.blogspot.com


0 Response to "Carboxylic Acid Derivatives Reactivity Order"
Post a Comment